Medallion Architecture
Medallion architecture is a data design pattern commonly used in modern data lakes and data warehouses, particularly in cloud-based environments.
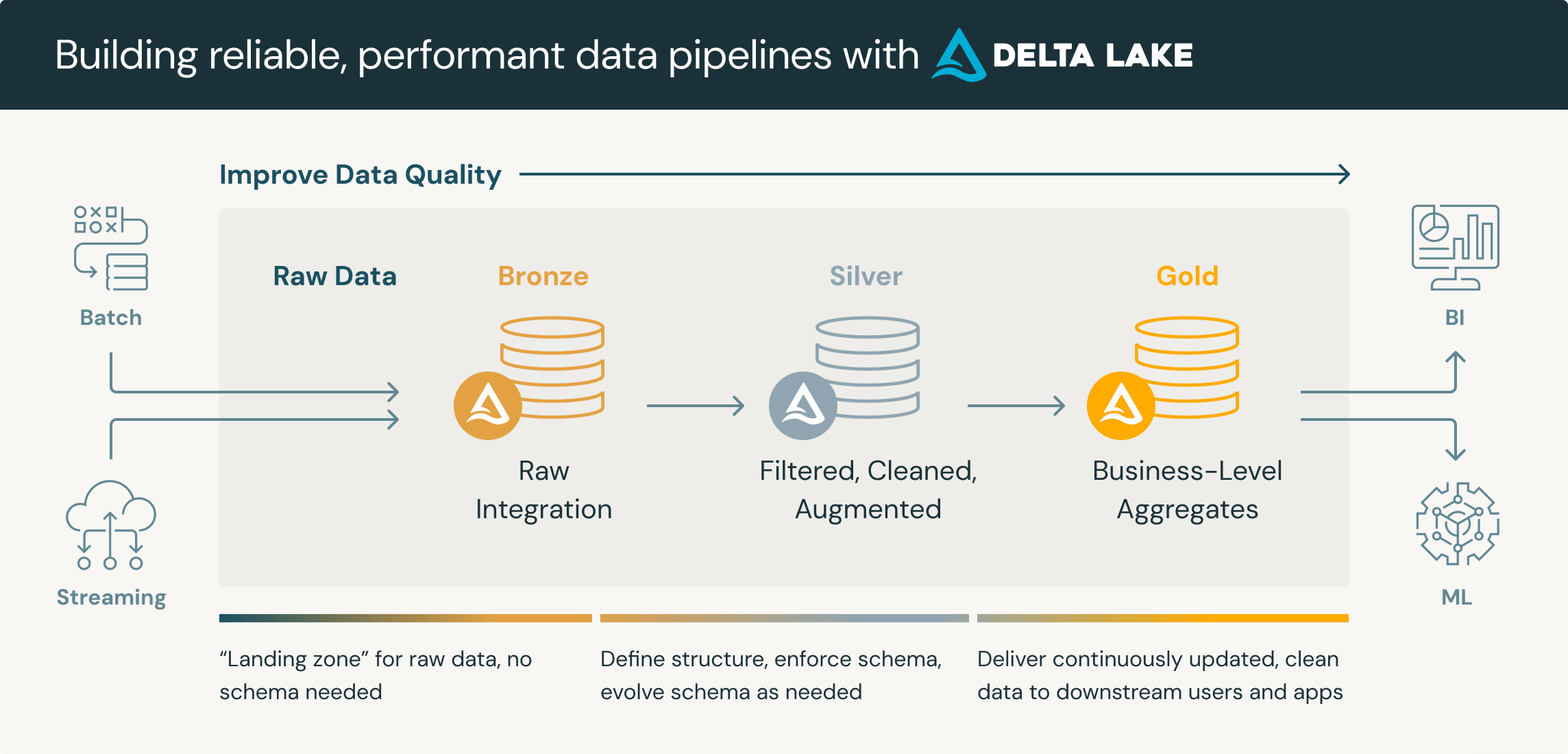
A medallion architecture is a data design pattern used to logically organize data in a lakehouse, aiming to incrementally and progressively improve the structure and quality of data as it flows through each layer of the architecture (from Bronze ⇒ Silver ⇒ Gold layer tables).
The Three Tiers
Bronze (Raw)
- Contains raw, unprocessed data.
- Typically a 1:1 copy of source system data.
- Preserves the original data for auditability and reprocessing if needed.
- Often stored in formats like JSON, CSV, or Avro.
Silver (Cleaned and Conformed)
- Cleansed and conformed version of bronze data.
- Applies data quality rules, handles missing values, deduplication.
- Often includes parsed and enriched data.
- Typically stored in a more optimized format like Parquet or Delta.
Gold (Business-Level)
- Contains highly refined, query-ready data sets.
- Often aggregated and joined from multiple silver tables.
- Optimized for specific business domains or use cases.
- Can include star schemas, data marts, or wide denormalized tables.
Key Principles
- Data flows from Bronze → Silver → Gold
- Each tier adds value and improves data quality
- Promotes data governance and lineage tracking
- Enables self-service analytics at different levels of refinement
Benefits
Flexibility: Supports various data processing needs
Scalability: Easily accommodates growing data volumes
Governance: Improves data lineage and auditability
Performance: Optimizes query performance on refined data sets
Reusability: Allows multiple downstream applications to use appropriately refined data