Why Surrogate Keys are Important
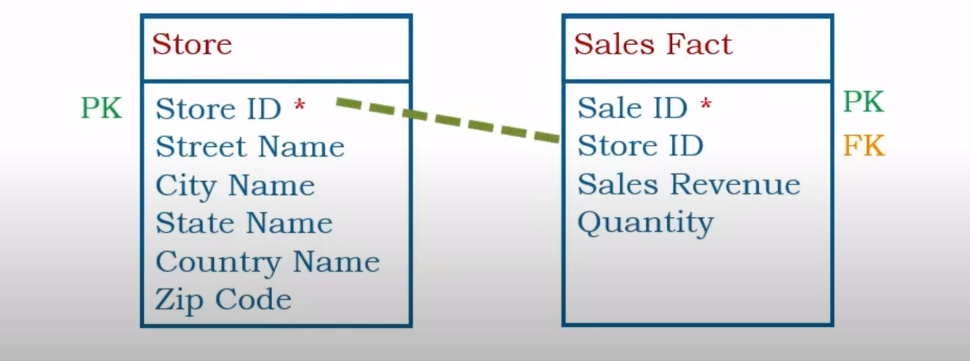
Example of Primary / Foreign Keys
Lets have a sample data
| StoreID * | Street | City | State | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1001 | 24th Blvd | Phoenix | AZ | USA |
| S1002 | 21 Bell Road | Miami | FL | USA |
| S1003 | Main Street | New Port | CA | USA |
StoreID is Natural Key (PK) It has a meaning S stands for Store 1001 means its the first store.
What is the issue now ?
When data changes (Slowly Changing Dimension we will cover in next chapter) how to handle the change.
Situation 1: Store 1 moves to new location or store is closed for sometime and opened under new franchise.
| StoreID * | Street | City | State | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1001 | 24th Blvd | Phoenix | AZ | USA |
| S1002 | 21 Bell Road | Miami | FL | USA |
| S1003 | Main Street | New Port | CA | USA |
| S1001 | 1st Street | Phoenix | AZ | USA |
Situation 2: When acquiring competitive business (say Target buys KMart), the Natural Keys dont make sense now.
| StoreID * | Street | City | State | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1001 | 24th Blvd | Phoenix | AZ | USA |
| S1002 | 21 Bell Road | Miami | FL | USA |
| S1003 | Main Street | New Port | CA | USA |
| 233 | South Street | New Brunswick | NJ | USA |
| 1233 | JFK Blvd | Charlotte | NC | USA |
These business decisions / changes have nothing to do with the Technology.
How to Overcome this issue?
Add Surrogate Keys (running sequence number)
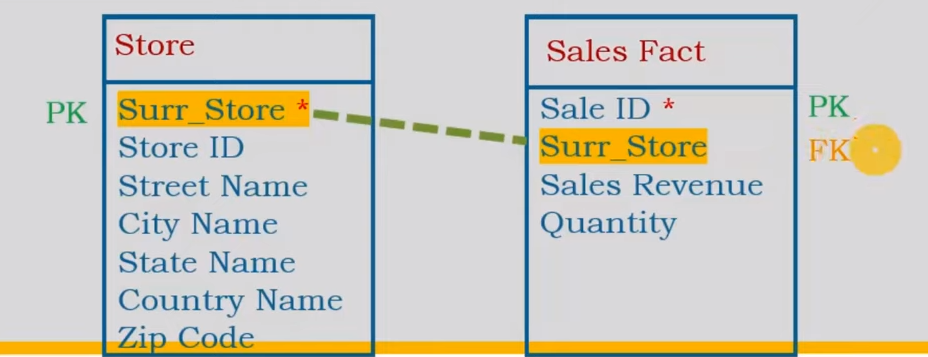
| Surr_Store * | StoreID | Street | City | State | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S1001 | 24th Blvd | Phoenix | AZ | USA |
| 2 | S1002 | 21 Bell Road | Miami | FL | USA |
| 3 | S1003 | Main Street | New Port | CA | USA |
| 4 | 233 | South Street | New Brunswick | NJ | USA |
| 5 | 1233 | JFK Blvd | Charlotte | NC | USA |
Properties of Surrogate Keys
- Numerical
- Sequential
- Meaningless Simple Number
Adv of Surrogate Keys
- Constant Behavior (will not change based on Business need)
- Integration is easier.
- Faster Query Performance. (because of Integer values)
- Future records (every other column can be NULL still ID is available)
Its a good practice to have Surrogate Key in DataWarehouse Dimension & Fact tables.